IntellaNOVA Newsletter #22 — From Elevating Your Data Game with Microsoft Fabric to Foundation Models, Snowflake Iceberg Tables, and Cortex Search
Revolutionizing Enterprise AI: 5 Game-Changing Use Cases Leveraging Snowflake Cortex AI’s Long Context Window
Imagine a life sciences company with millions of customer interactions stored in Snowflake’s AI Data Cloud, analyzing entire customer journeys, from chat logs and call transcripts to purchase history and social media interactions — all in one context. Thanks to Snowflake’s Cortex AI and its long context window capabilities, this kind of comprehensive analysis is now possible. In the past, large language models (LLMs) were limited by small context windows, requiring complex data chunking and reducing efficiency. However, modern LLMs with extended context windows, like those in Cortex AI, can process vast amounts of data in one go, opening new possibilities for enterprises. From enhancing customer support by providing personalized solutions, to detecting fraud by analyzing complex transaction data, Cortex AI revolutionizes how businesses handle data. Its long context window also supports advanced anomaly detection in IoT data, in-depth document analysis for legal and compliance purposes, and personalized learning programs by analyzing employees’ entire learning history. As more companies adopt these tools, the potential for innovation in data analysis and decision-making is greater than ever.
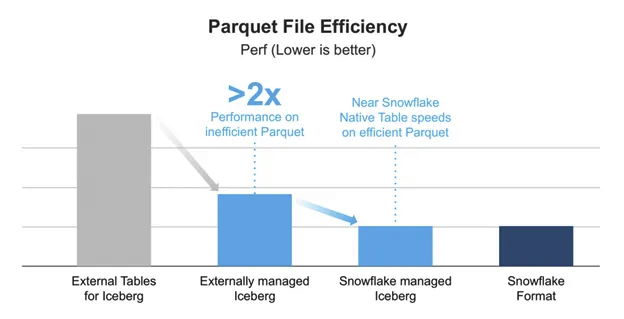
Unlock your Data Potential with Snowflake Iceberg Tables
Snowflake continues to innovate in data storage and compute optimization, and its recent support for the Iceberg table format, now in public preview, is a major advancement. Iceberg tables represent a shift in how data is managed, allowing Snowflake to access data stored externally in public cloud object storage like Amazon S3, Google Cloud, or Azure using the Apache Iceberg format. These tables combine Snowflake’s performance with external storage flexibility, making them ideal for hybrid architectures and data lakes while optimizing storage costs. Built on the Apache Iceberg specification, Iceberg tables offer advanced features like ACID transactions, schema evolution, hidden partitioning, and table snapshots. While still in public preview with some limitations compared to native Snowflake tables, this feature promises to enhance data management and governance, especially for organizations with existing data lakes.
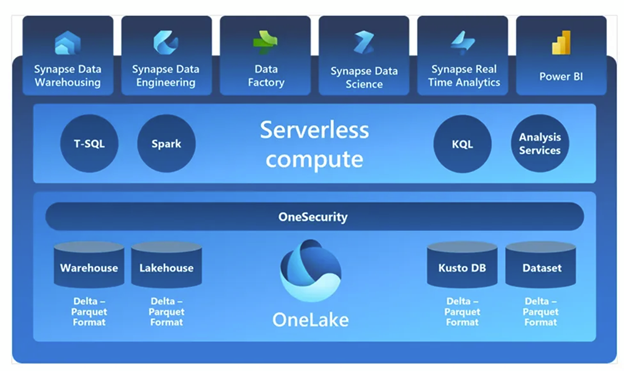
Elevate Your Data Game with Microsoft Data Fabric
At the Gartner Data and Analytics Summit, there was immense interest in Microsoft’s Data Fabric, with six out of ten visitors asking about it, despite its recent launch in November 2023. Microsoft Fabric is a unified, cloud-based SaaS platform that integrates tools like Data Factory, Synapse Data Warehouse, and Power BI, built on an open lake-centric design using OneLake as its central multi-cloud repository. It provides a modern data architecture combining data mesh, data fabric, and data hub principles, offering seamless data management and analytics across platforms like AWS and Azure. With features such as ACID transactions, AI integration, and pre-integrated Azure services, Microsoft Fabric enhances scalability and simplifies workflows. While migration challenges may arise, particularly for on-premises solutions, the platform’s capacity-based pricing and innovative capabilities promise to transform how organizations manage data and analytics.
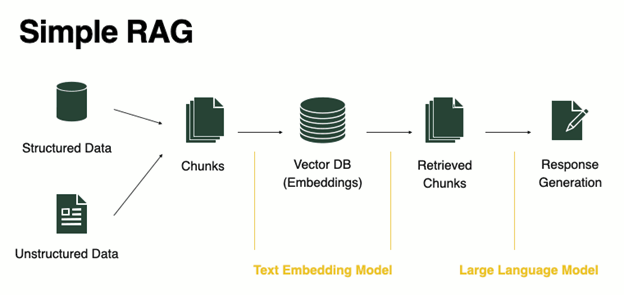
Unlocking the Power of RAG: Balancing Instant Insights with Security — Expert Insights from Databricks Summit
At the Databricks Summit, I engaged in insightful discussions with AI/ML leaders on the challenges of securing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. These conversations, featuring experts like Sanjeev Mohan, Saket Saurabh, Kamal Maheshwari, and others, underscored the balance between democratizing data through Large Language Models (LLM) and RAG and the rising security risks associated with real-time data access. While these technologies offer transformative potential by enabling instant insights, they also introduce security vulnerabilities, especially in managing vast data queries. The unpredictability of RAG poses significant challenges to existing access management workflows, highlighting the urgent need for innovation in securing these systems. Without robust solutions, the benefits of LLM + RAG could be overshadowed by security concerns, making it crucial for the data community to address these issues collectively and urgently.