Generative AI: The Double-Edged Sword of Innovation and Misinformation
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, offering unprecedented capabilities in creating realistic and synthetic content. Yet, with this revolutionary potential comes significant security challenges, especially when it comes to the production of hyper-realistic fakes. As we delve into this complex landscape, it becomes clear that while generative AI holds promise, it also opens the door to misuse in ways that can profoundly impact society.
The Dual-Edged Sword of Generative AI
Generative AI models, trained on vast datasets of text, images, or videos, can generate new content that closely mimics reality. This capability can be harnessed for positive innovations but also poses a risk when used maliciously.

How Generative AI Creates Fakes
Imagine a scenario where a deep fake video depicts a public figure making controversial statements they never actually made. Or consider synthetic media that fabricates entire events, blurring the line between reality and fiction. These are not just hypothetical situations; they represent real threats posed by generative AI. For example, a generative AI model trained on celebrity photos can create deep fakes that show these celebrities engaging in activities they never did. Similarly, synthetic media can fabricate audio or video recordings, creating realistic yet entirely fictional simulations of events.
Challenges of Generative AI Fakes
The primary security challenge with generative AI fakes is their potential to spread misinformation, propaganda, and disinformation. A well-crafted deep fake can damage reputations, influence elections, or create public panic. Beyond this, these fakes can impersonate real individuals, such as CEOs, to extract sensitive information or conduct fraudulent activities.
Other Critical Challenges
- Bias: Generative AI can reflect the biases present in its training data, leading to the creation of discriminatory or offensive content.
- Privacy: Fakes generated by AI can violate individual privacy, producing videos or audio that falsely depict people.
- Misinformation: AI-generated fakes can disseminate false information, creating scenarios that might incite fear or panic among the public.

Tackling the Security Flaw in Generative AI
Addressing these security flaws is no small feat. One approach involves developing advanced techniques to detect and authenticate generative AI fakes. However, as AI models grow more sophisticated, this becomes an increasingly complex task. Educating the public about the risks associated with generative AI is another crucial step. People need to understand that not everything they see or hear online can be trusted and should develop a critical approach to consuming information.
A Beacon of Hope: Innovative solutions to battle against generative AI fakes
Several leading companies are developing sophisticated tools to combat fake Generative AI (GenAI) content, particularly deepfakes and other forms of AI-generated disinformation. Here’s a closer look at what some of these companies offer:
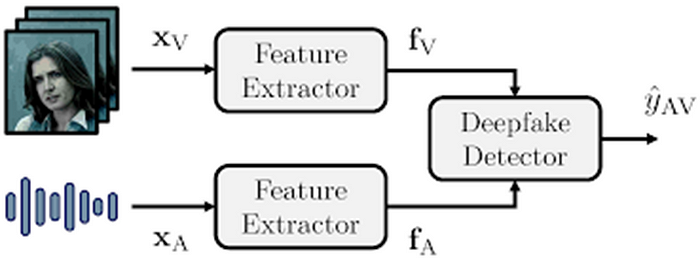
- Microsoft: Microsoft has implemented AI and machine learning-based solutions to detect and counter deepfakes. They utilize techniques like analyzing subtle inconsistencies in audio and visual data, such as unnatural facial movements or mismatched audio-visual cues. Their Video Authenticator tool, for example, can detect manipulated content by providing a confidence score that indicates the likelihood of a video being artificially altered. Microsoft also collaborates with various media and academic organizations to improve the reliability of their detection technologies and share best practices for combating AI-generated disinformation.
- Google: Google’s Jigsaw team focuses on addressing threats related to AI-generated disinformation. They have developed tools like Assembler, which helps journalists and fact-checkers identify manipulated images by comparing them to a database of known deepfakes. Google also invests in research to advance the understanding of AI manipulation techniques and improve detection algorithms. Their approach includes leveraging large datasets to train more accurate models and creating educational resources to help the public recognize and respond to disinformation.
- Adobe: Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) aims to promote digital content transparency and attribution. This initiative provides creators with tools to embed metadata in their work, detailing the content’s origin and any modifications made. Adobe’s software integrates these capabilities, enabling users to trace the history of digital media and verify its authenticity. The CAI also partners with industry leaders to establish a common framework for content attribution, helping to combat the spread of AI-manipulated media across platforms.
- Truepic: Truepic offers advanced image verification solutions to ensure the authenticity of digital content. Their Controlled Capture technology captures images and videos with verified metadata, preventing alterations. Truepic’s tools are used by journalists, law enforcement, and businesses to confirm the legitimacy of digital media. By providing a secure and verifiable way to document events, Truepic helps combat the proliferation of deepfakes and other AI-generated forgeries.
- Sensity: Sensity specializes in deepfake detection and visual threat analysis. Their platform uses AI to scan and analyze media for signs of manipulation, such as inconsistent lighting, unnatural facial expressions, or artifacts introduced during the creation of deepfakes. Sensity’s tools are used by social media platforms, governments, and security agencies to identify and mitigate the impact of AI-generated disinformation. Their ongoing research and development efforts aim to stay ahead of evolving deepfake technologies.
- Deepware: Deepware focuses on deepfake detection and response solutions. Their technology analyzes digital content for signs of manipulation, employing deep learning models trained on vast datasets of real and fake media. Deepware’s solutions are designed to be scalable, making them suitable for large organizations and platforms dealing with high volumes of user-generated content. They also provide APIs that integrate with existing systems to enhance detection capabilities and safeguard against AI-driven disinformation.
- Eyewitness Media Hub: Eyewitness Media Hub develops tools to verify the authenticity of user-generated content. Their focus is on providing resources and training for journalists and media organizations to accurately assess digital media. By offering tools that analyze metadata, check for inconsistencies, and cross-reference with known sources, Eyewitness Media Hub helps ensure the credibility of news and information. Their work is crucial in maintaining public trust in media during an era of rampant AI-generated disinformation.

These companies are at the forefront of developing technologies and frameworks to ensure that AI-generated content can be trusted and verified, thus mitigating the risks associated with deepfakes and other forms of AI-enabled disinformation. By leveraging their advanced solutions, organizations can better protect themselves and their audiences from the potential harms of fake GenAI conte
Conclusion
Generative AI stands as a powerful force capable of reshaping industries and pushing the boundaries of innovation. However, this power comes with significant responsibilities and risks. The ability of generative AI to create realistic fakes poses profound security challenges, from spreading misinformation to violating privacy and propagating biased content. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining technological advancements in detection and authentication with public education and awareness. As we navigate this new frontier, solutions from Microsoft, Google, Adobe, and others offer a promising path to harnessing the benefits of generative AI while minimizing the risk of misinformation.